AE1/AE3 is often referred to as “pan” cytokeratin, and is most commonly used to identify carcinomas, which present as morphologically undifferentiated malignant neoplasms. AE1/AE3 is also commonly used to identify micrometastatsis in sentinel lymph nodes, bone marrow, etc, and is probably the most used screening keratin antibody cocktail.
The AE1/AE3 cocktail contains CK1-8, 10, 14-16, and 19. It does not contain CK17 or CK18. This is why CAM5.2 may also used in a pan-CK cocktail. Given that AE1/AE3 is not completely sensitive for “all” cytokeratins, if a suspected carcinoma or undifferentiated tumor does not express AE1/AE3, then additional cytokeratin markers (e.g. CAM5.2 and/or 34BetaE12) may be helpful to maximize keratin expression sensitivity.
Moll, RT, et al. Cytokeratin expression in various tumors.
|
Tumor
|
CK8/CK18
|
CK19
|
CK7
|
CK20
|
CK5
|
|
Hepatocellular Ca.
|
+
|
+/-
|
+/-
|
+/-
|
=
|
|
Colorectal ACA
|
+
|
+
|
+/-
|
+
|
=
|
|
Stomach ACA
|
+
|
+
|
+/-
|
+/-
|
=
|
|
Pancreas Ductal ACA
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
+/-
|
+/-
|
|
Lung ACA
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
=
|
=
|
|
Breast Inv. Ductal
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
=
|
+/-
|
|
Endometrium ACA
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
=
|
+/-
|
|
Ovary ACA
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
=
|
=
|
|
RCC, Clear Cell Type
|
+
|
+/-
|
=
|
=
|
=
|
|
RCC, Papillary Type
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
=
|
=
|
|
RCC, Chromophobe
|
+
|
+/-
|
+
|
=
|
=
|
|
Mesothelioma
|
+
|
+
|
+/-
|
=
|
+
|
|
Lung, Small Cell Ca.
|
+
|
+/-
|
=
|
=
|
=
|
|
Merkel Cell Ca.
|
+
|
+
|
=
|
+
|
=
|
|
Urothelial Carcinoma
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
+/-
|
+/-
|
|
Squamous Cell Ca.
|
+/-
|
+/-
|
=
|
=
|
+
|
Key: “+/-“, focal staining in some cases. “=“, negative, “+”, positive.
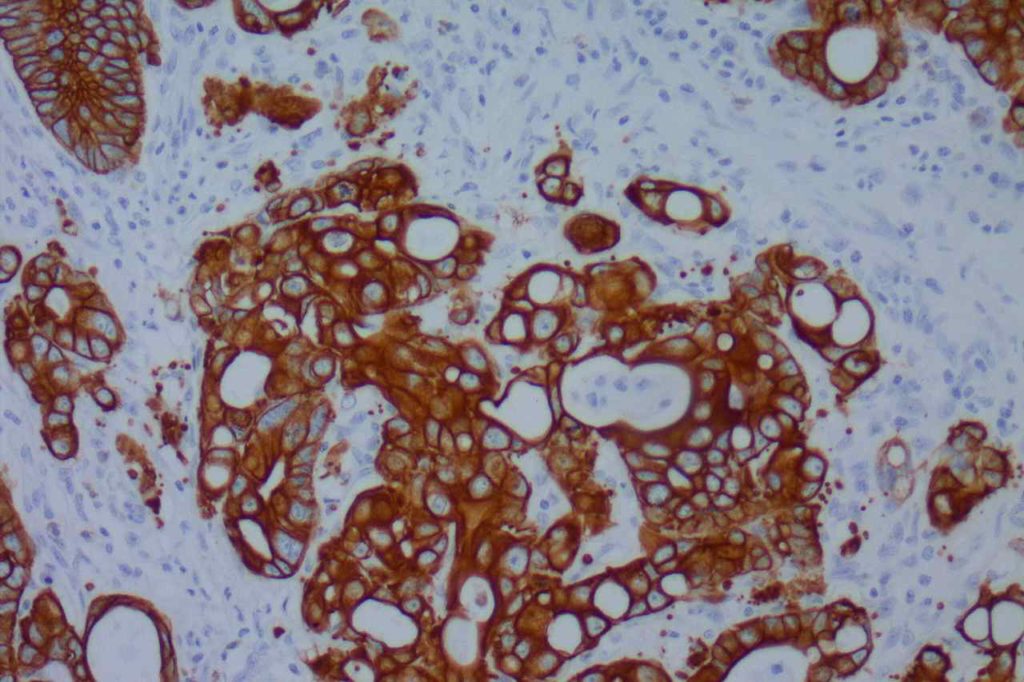
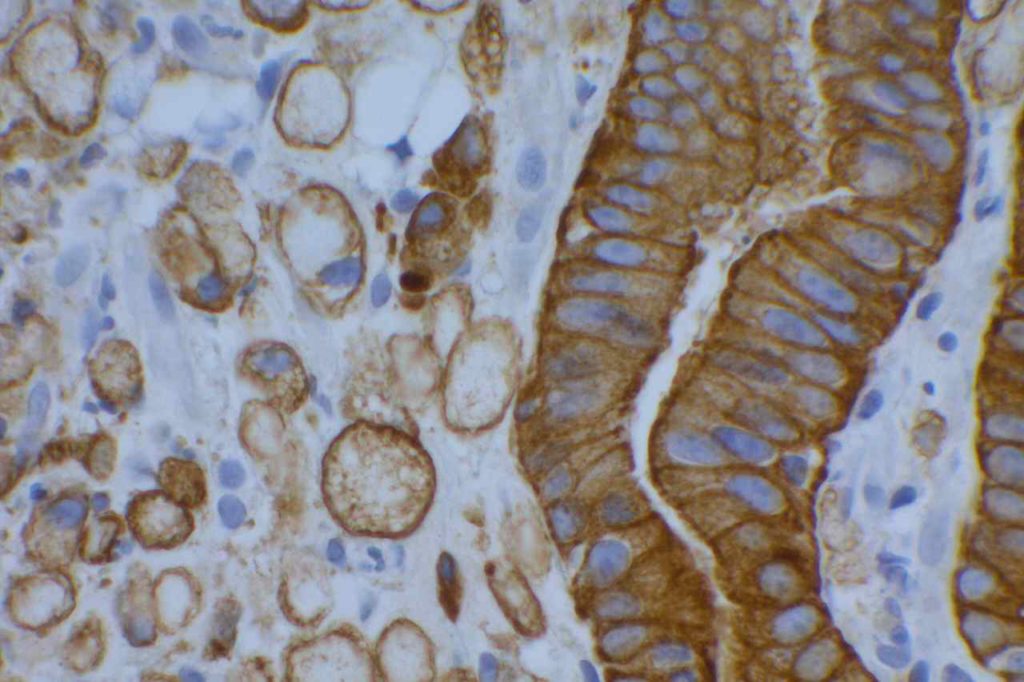
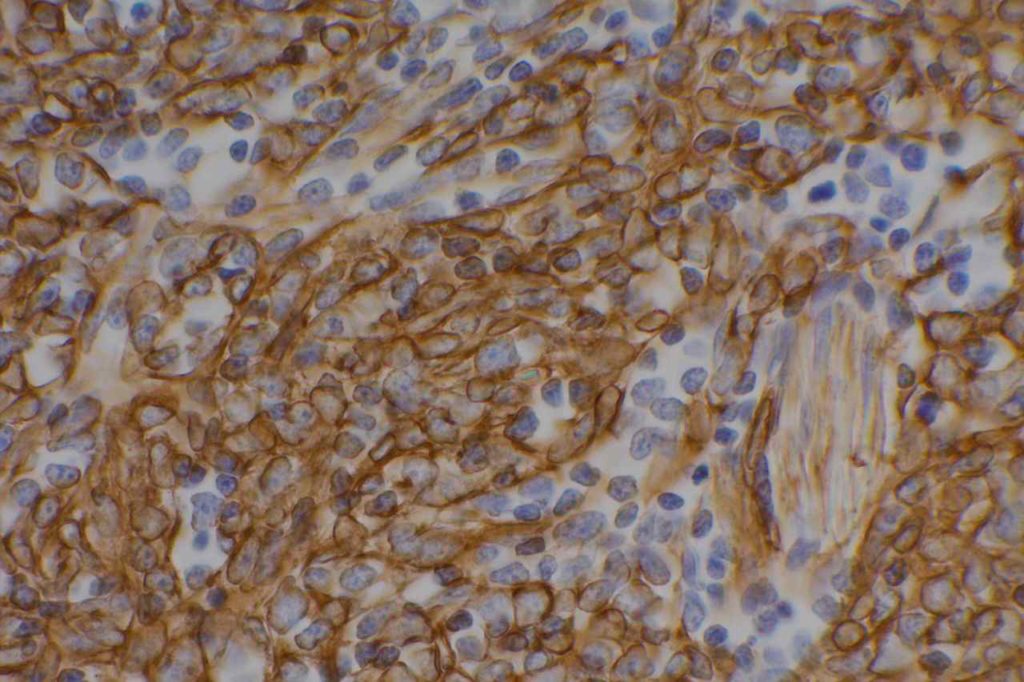
Microscopic Images
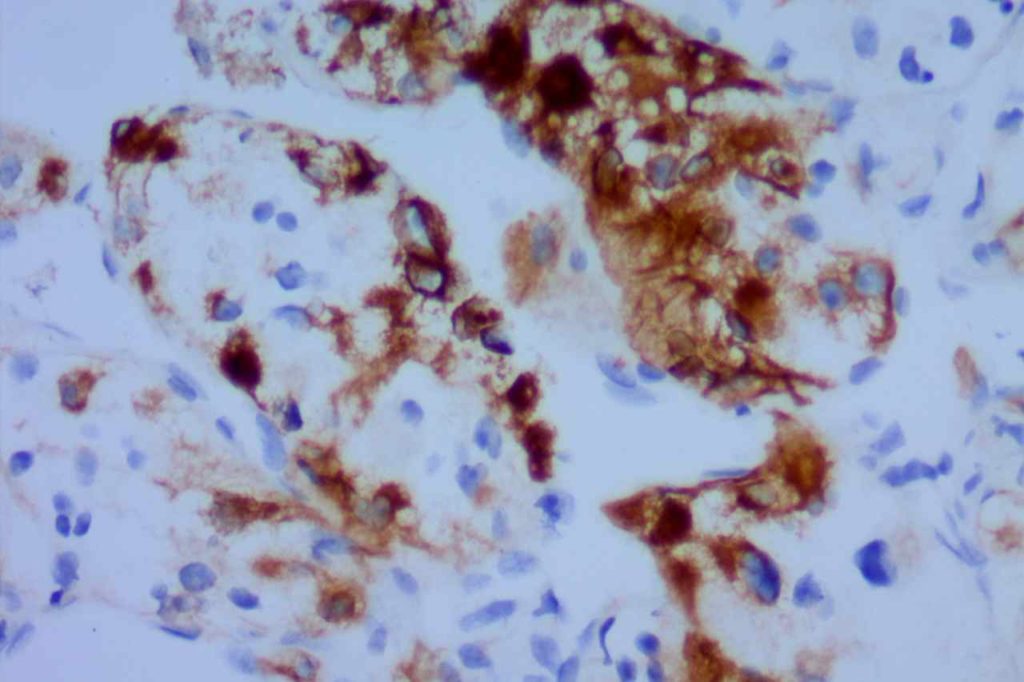
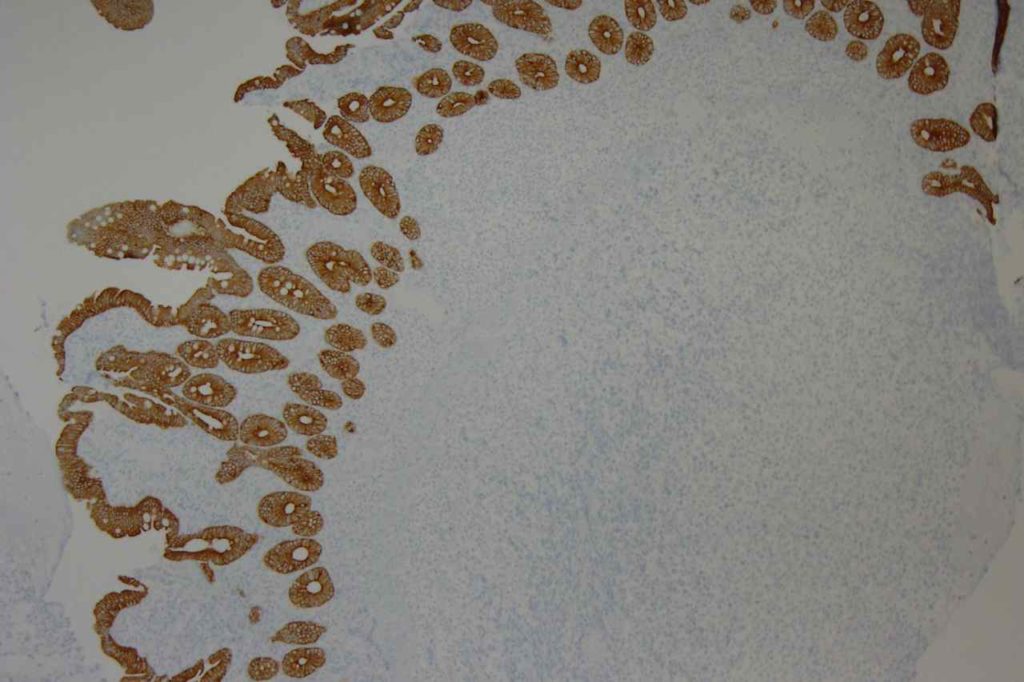
References:
Miller, RT, “Cytokeratin AE1/AE3”. ProPath The Focus Immunohistochemistry. November 2003. http://www.ihcworld.com/_newsletter/2003/focus_nov_2003.pdf
Hadi, AIMM Annual Meeting, “The Thirty Most Important Antibodies”, presentation, 2011.
Moll, R., Divo, M., & Langbein, L. (2008). The human keratins: biology and pathology. Histochemistry and Cell Biology, 129(6), 705–733. doi:10.1007/s00418-008-0435-6