MUM-1/IRF-4 (multiple myeloma oncogene 1/Interferon Regulatory Factor-4) is a nuclear transcription factor, which is expressed in late stage germinal center cells (as bcl-6 expression begins to be down-regulated) and post-germinal center lymphocytes/plasma cells. Activated T-cells may also express MUM-1.
MUM-1 is most commonly used as part of an algorithm to subtype diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) into germinal center (GCB) and non-germinal center (non-GCB) phenotypes. MUM-1 positive DLBCLs (that are CD10 negative) are considered “non-germinal center” (analogous to post-germinal center by gene analysis), which have a poorer prognosis compared to a “germinal center” immunophenotype (Hans’ algorithm). In the Hans’ classifier, MUM-1 positivity is defined as expression in >30% of cells.
MUM-1 is not expressed in epithelial cells, but expression has been identified in approximately 25% of melanomas. In limited situations, it may be helpful in confirming plasma cell origin of CD138 positive cells, in which kappa/lambda does not stain. CD138 will often stain cells of epithelial origin.
MUM-1 Expression Pattern
- Plasma Cells (benign & neoplastic)
- DLBCL
- Activated T-cells
- T-cell Lymphomas (subset)
- Most subtypes of B-cell lymphomas
- PTLD
- Follicular Lymphoma (mainly subset of grade 3)
- Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (positive)
- Nodular Lymphocyte Predominate Hodgkin Lymphoma (negative, ~25% of cases may show dim expression in <30% of neoplastic cells)
Photomicrographs
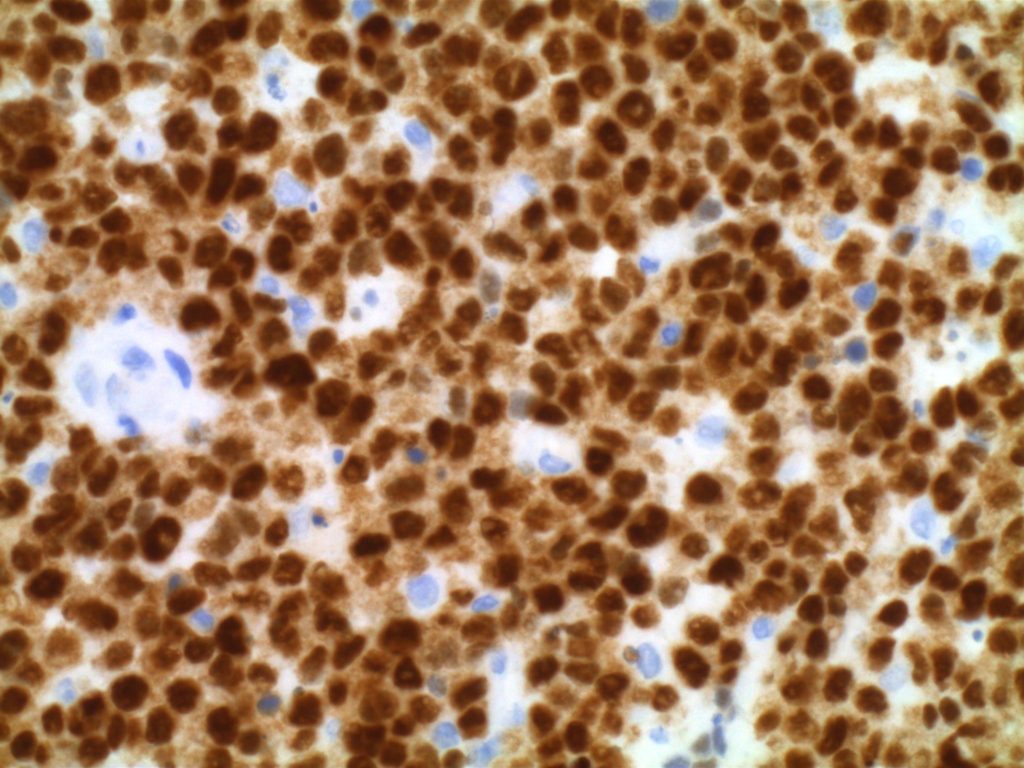
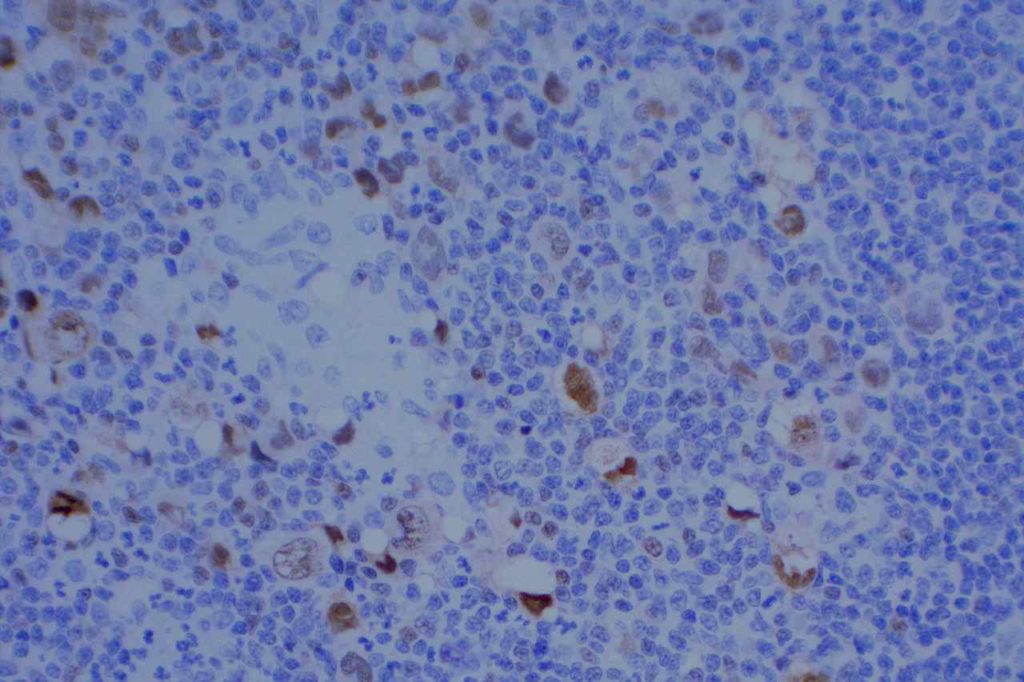

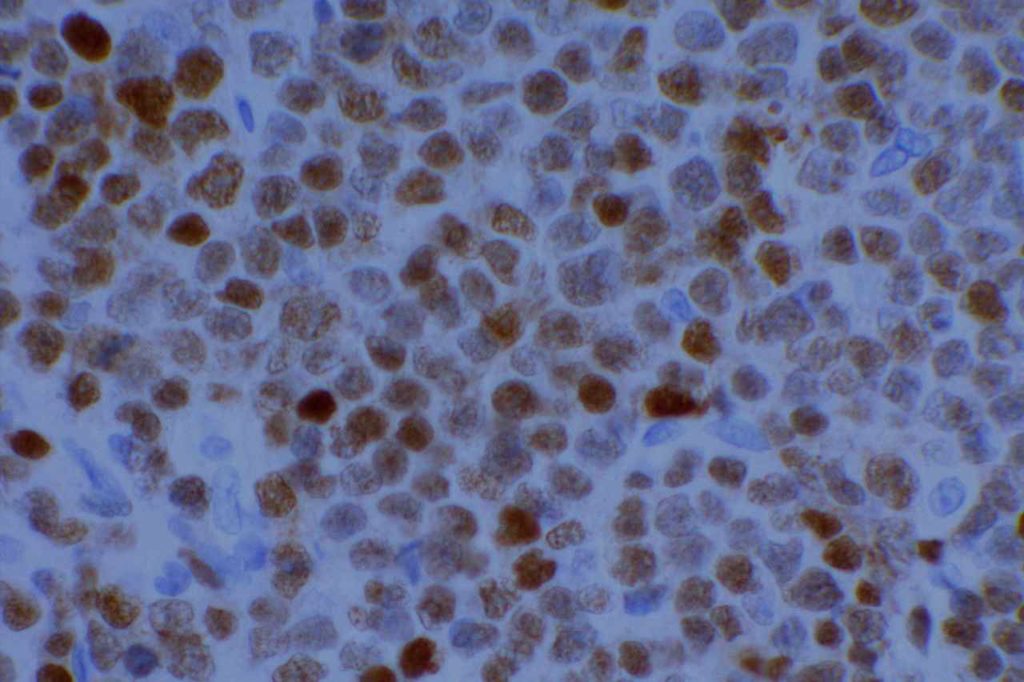
References
Natkunam Y, Warnke RA, Montgomery K, Falini B, van De Rijn M. Analysis of MUM1/IRF4 protein expression using tissue microarrays and immunohistochemistry. Mod Pathol. 2001;14: 686–694. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880373
Herbeck R, Teodorescu Brînzeu D, Giubelan M, Lazăr E, Dema A, Ioniţă H. B-cell transcription factors Pax-5, Oct-2, BOB.1, Bcl-6, and MUM1 are useful markers for the diagnosis of nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52: 69–74.
Haarer CF, Roberts RA, Frutiger YM, Grogan TM, Rimsza LM. Immunohistochemical classification of de novo, transformed, and relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into germinal center B-cell and nongerminal center B-cell subtypes correlates with gene expression profile and patient survival. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130: 1819–1824.
Berglund M, Thunberg U, Amini R-M, Book M, Roos G, Erlanson M, et al. Evaluation of immunophenotype in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its impact on prognosis. Mod Pathol. 2005;18: 1113–1120. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800396
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004;103: 275–282. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-05-1545
Alizadeh AA, Elsen MB, Davis RE, Ma C. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000.
Bone Marrow IHC. Torlakovic, EE, et. al. American Society for Clinical Pathology Pathology Press © 2009. pp. 221.